- May 27, 2024
- Aws Al-Ani
- Uncategorized
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is a common health concern that is often linked to diet, including the consumption of a low carb diet. It is a condition characterized by an excessive accumulation of fat in the liver.
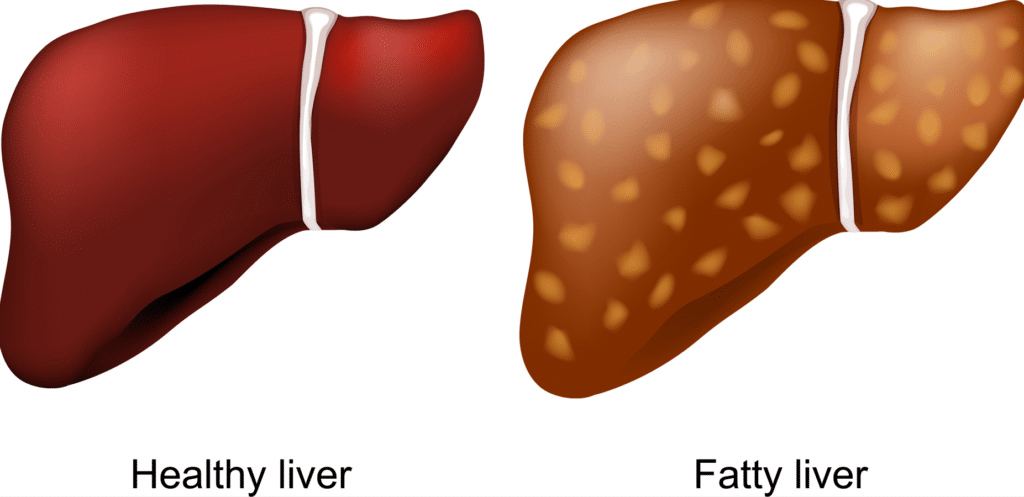
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease occurs when more than 5% to 10% of the liver’s weight is made up of fat. This condition can lead to significant health problems if left untreated. However, it’s important to note that fatty liver disease can be reversed, especially with dietary changes such as adopting a low carb diet.
Causes and Symptoms
The most common causes of fatty liver disease include obesity, insulin resistance, high blood cholesterol, and excessive alcohol intake. Less common causes include certain medications, underactive thyroid, and complications that develop late in pregnancy.
Fatty liver disease often doesn’t cause symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include fatigue, discomfort in the upper right belly area, and unexplained weight loss. More serious symptoms that may indicate advanced fatty liver disease include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), bruising, dark urine, swollen abdomen, vomiting blood, black stools, and itchy skin.
Types of Fatty Liver Disease
There are two main types of fatty liver disease: alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Alcoholic fatty liver disease is caused by heavy alcohol use. The liver’s job is to break down alcohol, and if you drink more than it can process, it can become badly damaged. Early damage to the liver causes fat to deposit onto the liver, resulting in alcoholic fatty liver disease. If left untreated, it can progress to more severe conditions like alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a liver problem that affects people who drink little to no alcohol. In NAFLD, too much fat builds up in the liver. It is seen most often in people who are overweight or obese. NAFLD is linked to several health problems including genetics, overweight or obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and high levels of fats, especially triglycerides, in the blood.
Find out more
In conclusion, understanding fatty liver disease and its connection to diet, particularly a low carb diet, is crucial for maintaining liver health. By making dietary changes and leading a healthy lifestyle, it’s possible to manage and even reverse this condition.
The Role of Diet in Liver Health
Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining liver health and preventing liver diseases. A balanced diet is essential for optimal liver function as it provides the necessary nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that support liver health.
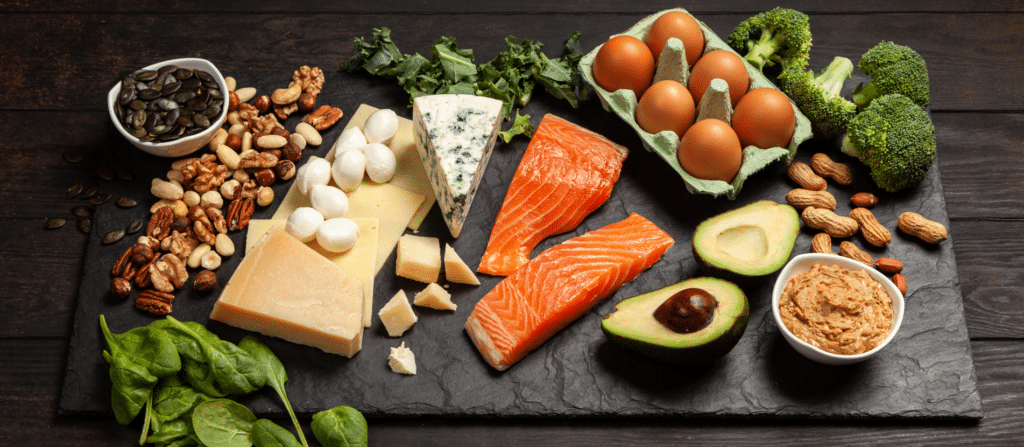

Impact of Diet on Liver Health
Your liver processes everything you eat and drink every single day. Too much sugar, or too much alcohol, can cause fat to build-up in your liver. When the liver is fatty, it cannot perform all of its many functions, and it can become more damaged over time.
Foods That Contribute to Fatty Liver Disease
Eating too many ultra-processed foods is linked to fat buildup in the liver. Common ultra-processed foods include packaged cakes, cookies, sweets, chips, and other snack foods. The biggest risk factor for obesity that leads to fatty liver is having a diet high in sugars and processed foods. Dietary changes inducing weight loss and adding nutrient-dense, antioxidant-packed foods, such as vegetables, red meat, chicken, eggs, and fish can reverse or prevent the progression of the disease. Limiting carbohydrates, simple sugars, high-fructose corn syrup, polyunsaturated fats, and processed foods is also important.
How a Balanced Diet Can Maintain Liver Health
Maintaining a healthy liver requires a balanced diet that includes vegetables, red meat, chicken, eggs, and fatty fish. Furthermore, it is crucial to NOT choose polyunsaturated fats. A low carb diet — which focuses on eating a balance of proteins and vegetables — is a good regimen to follow for your liver.
In conclusion, understanding the role of diet in liver health, particularly in the context of a low carb diet, is crucial for maintaining liver health. By making dietary changes and leading a healthy lifestyle, it’s possible to manage and even reverse fatty liver disease.
Low Carb Diet | A Closer Look
A low carb diet is a dietary approach where the intake of carbohydrates is significantly reduced, and the body’s primary source of energy shifts from carbohydrates to fats. This diet primarily includes protein-rich whole foods, non-starchy vegetables, and natural fats. Foods high in carbohydrates such as bread, pasta, rice, and sugary foods are generally avoided.

The Role of a Low Carb Diet in Fatty Liver Disease
Research suggests that a low carb diet can be beneficial for people with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). This diet can help reduce liver fat, decrease insulin levels, suppress appetite, promote weight loss, and improve heart health markers. It’s important to note that the effectiveness of a low carb diet in managing fatty liver disease may vary among individuals.
How Does a Low Carb Diet Work?
The mechanism behind a low carb diet involves a metabolic state known as ketosis. When the intake of carbohydrates is low, the body starts using fat as its main fuel source due to limited access to glucose. This leads to the production of molecules called ketones, which are used as an alternative energy source throughout the body. This process of burning fat for energy instead of carbohydrates is the fundamental principle of a low carb diet.
Foods Included and Excluded in a Low Carb Diet
A low carb diet typically includes foods such as meat, fish, eggs, and non-starchy vegetables. Lower carb fruits, nuts, seeds, and high-fat dairy products can also be included. Foods that are generally avoided include grains, legumes, fruits, breads, sweets, pastas, and starchy vegetables.
Potential Health Benefits of a Low Carb Diet
Apart from potentially improving liver health, a low carb diet can also offer other health benefits. These include weight loss, improved blood sugar management, and reduced risk of heart disease. However, the benefits can vary among individuals and it’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting a new diet.
Low Carb Diet and Its Impact on Fatty Liver Disease

The Connection Between a Low Carb Diet and Fatty Liver Disease
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a condition where excess fat is stored in the liver. It’s estimated to affect about 25% of the population in most Western countries, and as many as 1 billion people worldwide. A low carb diet has shown promise in managing and even reversing this condition.
Research suggests that a low carb diet can help reduce liver fat, decrease insulin levels, suppress appetite, promote weight loss, and improve heart health markers. This is because when the intake of carbohydrates is low, the body starts using fat as its main fuel source due to limited access to glucose. This leads to the production of molecules called ketones, which are used as an alternative energy source throughout the body.
Practical Tips for Incorporating a Low Carb Diet into Your Lifestyle
Adopting a low carb diet can be a significant lifestyle change. Here are some practical tips to help you make the transition:
Learn About Different Types of Carbs: Before starting a low carb diet, it’s important to understand the difference between good and bad carbs.
Click here to check out an effective diet for fighting Inflammation
Interested In Speaking To a Low Carb GP?
We are more than happy to assist you on your journey, feel free to book an appointment with us using the button below:
Thank You for Reading!
References:
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease:
- https://www.verywellhealth.com
- https://www.healthdirect.gov.au
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org
- https://alcohol.org
- https://www.mayoclinic.org
- https://microsoftstart.msn.com
- https://www.msn.com
The Role of Diet in Liver Health:
- https://www.healthline.com
- https://liver.org.au
- https://www.hep.org.au
- https://www.healthline.com
- https://www.singlecare.com
- https://liver.org.au
- https://www.verywellhealth.com
- https://www.goodrx.com
- https://health.clevelandclinic.org
- https://www.healthifyme.com
- https://www.darwynhealth.com
Low Carb Diet | A Closer Look:
- https://www.dietdoctor.com
- https://www.healthline.com
- https://www.mayoclinic.org
- https://www.verywellfit.com
- https://www.dietdoctor.com
- https://fattyliverdisease.com
- https://www.verywellhealth.com
- https://www.liverdoctor.com
- https://www.gu.se
- https://www.healthline.com
- https://en.wikipedia.org
- https://www.webmd.com
Low Carb Diet and Its Impact on Fatty Liver Disease:

